Spring5现处在第四个预发布版,正式版将要发布了,它带来的一大特性就是响应式框架Spring WebFlux。默认使用ProjectReactor框架。因此。本文通过ProjectReactor中的Flux,来学习使用该框架,以及了解其传递的思想。
本文基于Reactor3.1 rc1
Reactor官方地址http://projectreactor.io/,官方文档写的十分详细,如果您有不错的英文能力,建议直接阅读官方文档。
Spring WebFlux 实践
首先,为大家带来一个使用了ProjectReactor的例子,该例子使用Spring Boot 2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT。因Spring Boot推荐默认配置(约定)优先,可以极大减少大量的重复的模版化代码,简化搭建过程。
Spring Boot 2.0.0稳定版还未出,不过也快了,目前处在第四个里程碑版本。
step1:搭建环境
spring boot部分工具如idea提供了可视化操作,选择reactive-web模块即可(你也可以多选一些你需要的模块),如果没有可视化的工具,也可访问官网的开始页面https://start.spring.io/,或者在pom中引入一下模块(web开发主流仍是maven,所以未采用gradle)
1 | |
step2:编写处理类
编写一个简单的处理类,TestHandler
1 | |
step3:编写路由
spring webflux也提供了函数试的路由配置,如下
1 | |
step4:测试,验证
当浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/test,得到结果:this is null! from server webflux! 当浏览器输入http://localhost:8688/test?data=hi,得到结果:hi! from server webflux!
我的webflux项目地址:GitHub
深入学习
看过实践后,你会发现有大量的使用Flux和Mono,它们是什么呢?
Flux
静态方法
Flux一般通过静态方法构造,所以先看看它的静态方法。
combineLatest
public static <T,V> Flux
构建一个Flux,混合由多个的发布者发布最新事件.
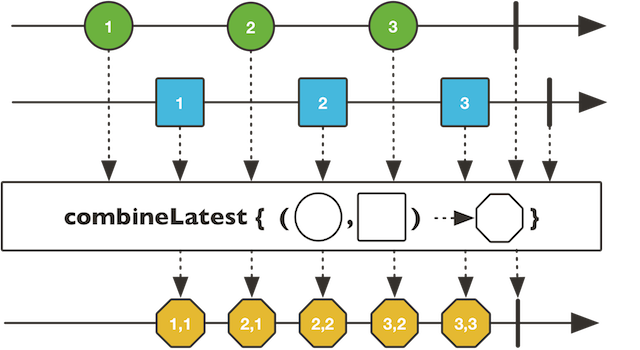
Type Parameters:
T - 表示发布者的事件类型
V - 被混合者混合后的类型
Parameters:
sources - 发布者,提供事件
combinator - 混合者,接受最新的事件,处理并传递给下游。
Returns: 一个以Flux为基础的混合流
不同的参数方法很多,这里都只展示一个。
concat
public static
用于连接一个流。与combineLatest不同的是,concat都是在前一个流完成后在连接新的流。而combineLatest,则哪个事件最先到的,哪个先处理。
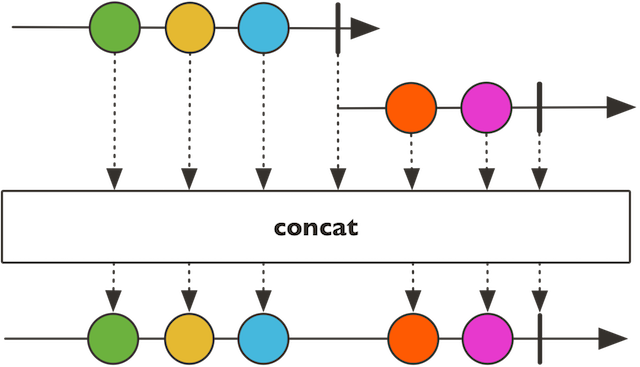
Type Parameters:
T - 事件的类型
Parameters:
sources - 一系列的发布者
Returns: 一个新的Flux连接了所有的发布者,并传递给下游
concatDelayError
拥有与concat类似的方法,不同的是,遇到错误不提前拦截,而是等到最后发布的事件处理完成后
create,push
public static
通过FluxSink API,以同步或者异步方式创建Flux。
例如:
1 | |
这是非常有用的,如果一个流,需要动态添加或者移除其他的多个事件,通过异步的api。而且,你将不必担心被取消和背压。
create(Consumer<? super FluxSink
push方法用处与使用方式与create几乎一致,它们唯一的区别在于CreateMode类型 create为PUSH_PULL,而push为PUSH_ONLY,从文档中也可以一个为多线程一个为单线程
backpressure(背压)概念的理解
这里,我摘自一位大神的话,背压是指在异步场景中,被观察者发送事件速度远快于观察者的处理速度的情况下,一种告诉上游的被观察者降低发送速度的策略。简而言之,背压是流速控制的一种策略。
更多的背压到http://www.jianshu.com/p/2c4799fa91a4这里不多做介绍了
defer
public static
这个方法提供了一种惰性策略,发布者不会一开始发布消息,直到订阅者创建实例.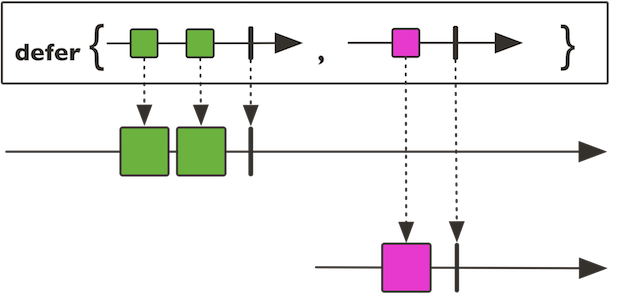
Type Parameters:
T - 发布者发布或订阅者接受的类型
Parameters:
supplier - 一个发布者的供应者,当订阅的时候回调
Returns: 一个惰性的Flux
empty
public static
创建一个不含任何事件的流.
error
public static
返回一个带着立即终止标识和错误信息的流
first
public static Flux first(Publisher<? extends I>… sources)
挑选出第一个发布者,由其提供事件。能有效避免多个源的冲突。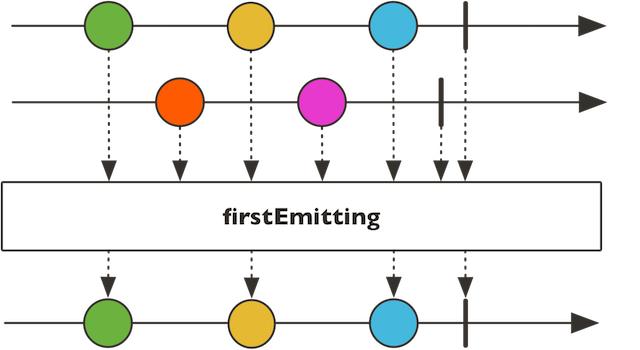
from
public static
public static
public static
从一个发布者创建一个flux流
fromArray,fromIterable,fromStream
public static
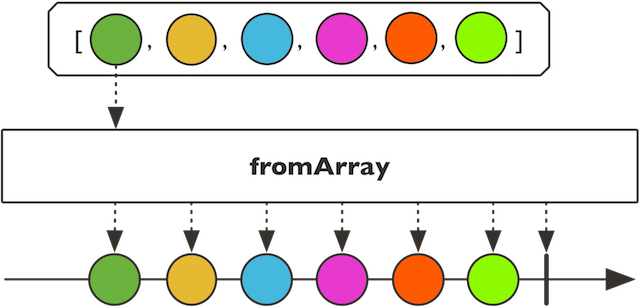
Type Parameters:
T - 数组的类型和Flux的类型
Parameters:
emmm.. - 数组,可迭代的元素,流
Returns: 新的flux流
generate
public static
Programmatically create a Flux by generating signals one-by-one via a consumer callback.
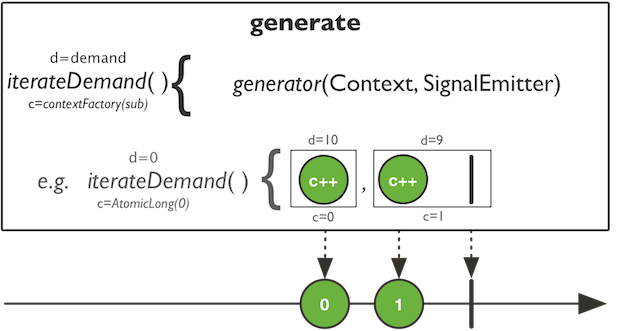
Type Parameters:
T - the value type emitted
Parameters:
generator - Consume the SynchronousSink provided per-subscriber by Reactor to generate a single signal on each pass.
Returns: a Flux
没看懂,好像是说,通过编程方式创建一个一对一的消费回调
interval
public static Flux
间隔一定的时间,发送事件。
Runs on the Schedulers.parallel() Scheduler.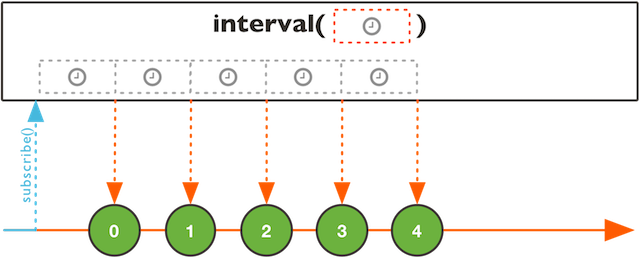
just
public static
创建一个包含一系列元素的flux流
merge
public static Flux merge(Publisher<? extends I>… sources)
混合多个流,和combineLatest类似,但它要求是同类型的流合并,combineLatest需要提供合并方式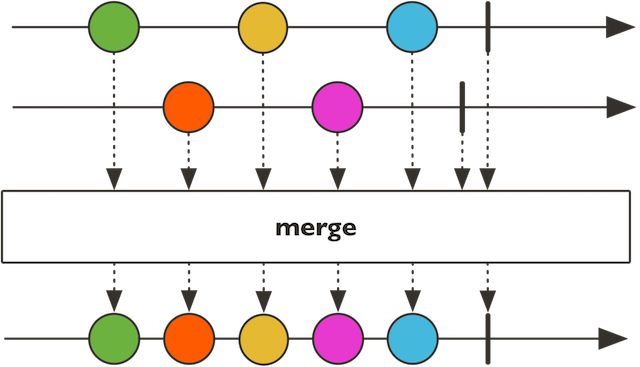
never
public static
Create a Flux that will never signal any data, error or completion signal.

Type Parameters:
T - the Subscriber type target
Returns:
a never completing Flux
看一看,不是很明白,该流的用处。
range
public static Flux
提供从start,到start + count的所有整数的flux流
switchOnNext
public static
从最新的发布者那里获取事件,如果有新的发布者加入,则改用新的发布者。
当最后一个发布者完成所有发布事件,并且没有发布者加入,则flux完成。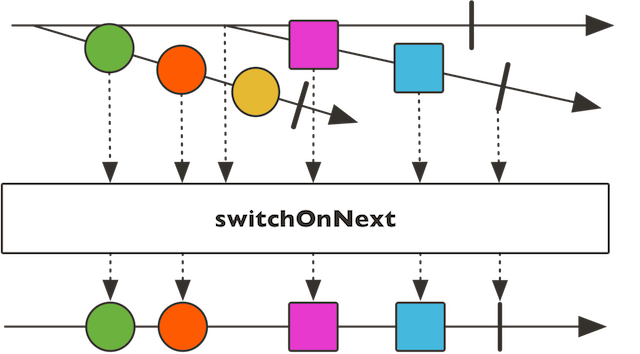
using
public static <T,D> Flux
Uses a resource, generated by a supplier for each individual Subscriber, while streaming the values from a Publisher derived from the same resource and makes sure the resource is released if the sequence terminates or the Subscriber cancels.
Eager resource cleanup happens just before the source termination and exceptions raised by the cleanup Consumer may override the terminal even.

zip
public static <I,O> Flux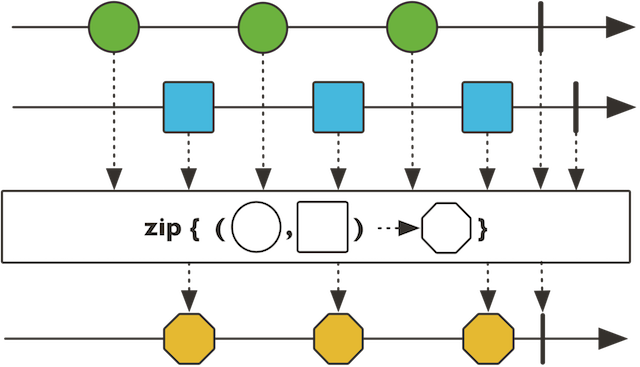
…
看一下下面的api
public static <T1,T2,T3,V> Flux
…
public static <T1,T2> Flux<Tuple2<T1,T2>> zip(Publisher<? extends T1> source1, lisher<? extends T2> source2)
public static <T1,T2,T3> Flux<Tuple3<T1,T2,T3>> zip(Publisher<? extends T1> source1, lisher<? extends T2> source2, lisher<? extends T3> source3)
…
ヽ(o_ _)o摔倒,我也是服了project reactor 官方。
常用的实例方法
静态的方法介绍完了,但是实例方法比静态方法多太多,所以这里只举常用的几种介绍
all,any,hasElement,hasElements
这几个方法调用,均返回包涵一个Boolean信号的Mono。
- all(Predicate<? super T> predicate)表示所有值均满足条件
- any(Predicate<? super T> predicate)表示存在一个值满足条件
- hasElement(T t)表示是否存在该值
- hasElements()表示是否拥有一个或多个元素
as,compose
public final
P as(Function<? super Flux
转化flux为一个目标类型。
官方例子:flux.as(Mono::from).subscribe()
将flux通过Mono.from函数转化为mono
public final
compose与as的区别是转化类型做了限制,必须继承Publisher,同时compose是惰性的。在很多时候,写法上没有差别如flux.compose(Mono::from).subscribe()
blockFirst,blockLast
阻塞至第一个或者最后一个值处理完成
butter系列
该系列实例方法很多,作用是将一系列元素,分成一组或者多组,该方法可用在按组批量操作上,例如,以时间间隔分组,批量添加数据。
cache
如其名缓存,相当于复制一份用于接下来的操作,而当前的流将会被缓存起来,用于之后的操作。
cancelOn
public final Flux
取消
cast
public final
checkpoint
用于检测当前节点,流中是否存在错误
collect系列
该系列实例方法,用于收集所有的元素到特定类型,如list、map等
处理完成时返回Mono
concatMap系列,flatMap系列
举例说明吧,[[1,2],[4,5],[6,7,8]] -> [1,2,4,5,6,7,8]起这种转化作用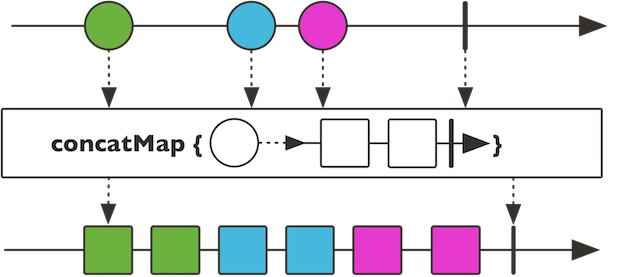
flatMap系列一样
concatWith
与concatMap不同,这是相加
defaultIfEmpty
public final Flux
distinct
public final Flux
去重,相对与jdk8,多了下面两种方法
public final
public final <V,C extends Collection<? super V>> Flux
do系列
还系列有doOnNext,doOnError,doOnCancel等等,均表示完成后触发
elementAt
返回某一位置的值,类型为Mono
filter
public final Flux
过滤出满足条件的
groupBy
public final 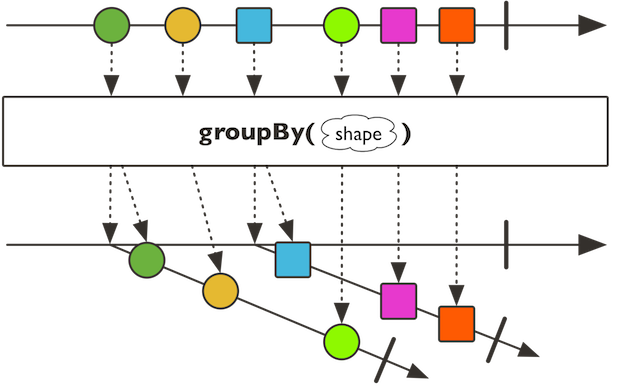
分组,根据提供的keyMapper
mark
标记一下,写到h接下来还有一些要写,暂时不写了,太累。。。先写会实践(实践提前放在开头,入门)
未完待续